Micro-vibrations are low amplitude disturbances generated by moving equipment onboard a spacecraft. These vibrations can really shake up and degrade the functionality of sensitive optical devices like cameras attached to the spacecraft bus. One possible consequence of this is the distortion and blurring of images captured from the spacecraft.
These micro-vibrations are typically less than 250 Hz, and a practical solution involves integrating vibration isolators between the spacecraft bus and the optical device or between the bus and the vibration source. Researchers from the Robotics and Design Lab, Indian Institute of Science (IISc) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), under the supervision of Ashitava Ghosal, have developed a two-radii Gough-Stewart platform (GSP)-based multi-axis vibration isolation system for spacecraft applications.
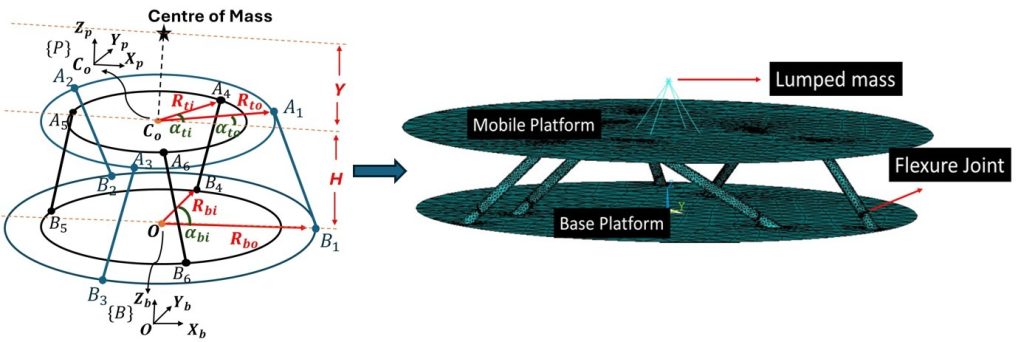
Typically, a GSP is a 6-DOF (degrees of freedom) parallel manipulator consisting of a mobile platform, a fixed base, and six legs with prismatic joints connecting these two platforms. In a typical application, the fixed base is attached to the spacecraft bus, the optical payload is mounted on the top mobile platform and the prismatic joints are replaced with dampers.
In a two-radii GSP, the anchor points on the two platforms are chosen to be along two radii. This design can help achieve dynamic isotropy, where resonance peaks corresponding to first six degrees of freedom are at one place (frequency) in the amplitude versus frequency curve. At resonant frequency, a medium vibrates at the highest amplitude, and having all of the six peaks at one place can effectively and equally damp all the modes together in a passive damping GSP.
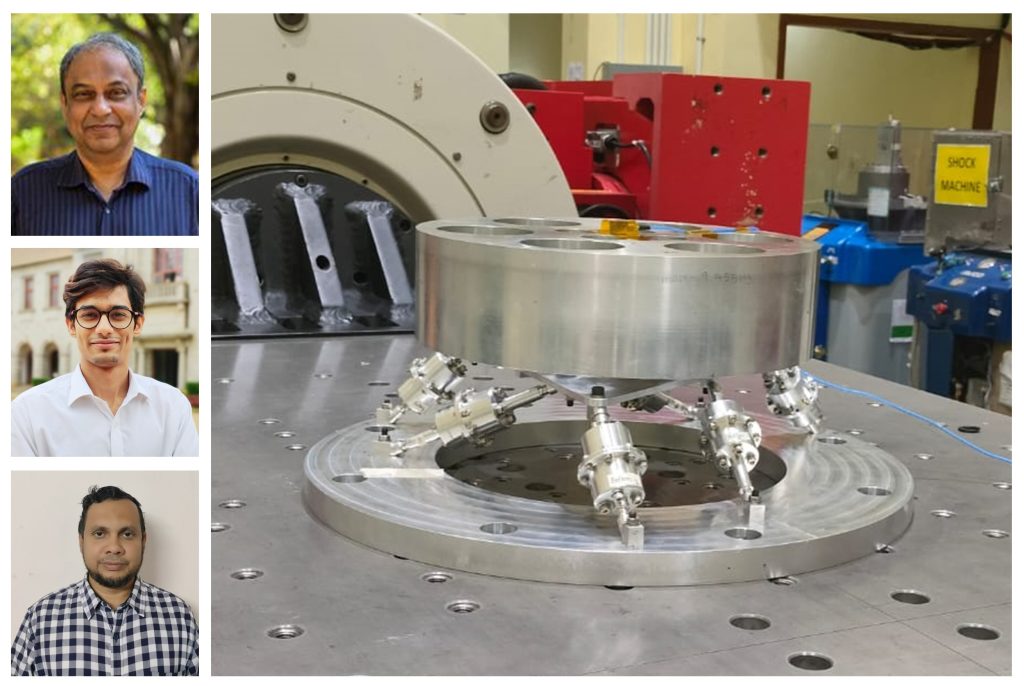
In the study published in Mechanism and Machine Theory, the researchers adopted a novel geometry-based approach to derive the dynamically isotropic configuration of the two-radii GSP. A prototype of the MGSP featuring flexural joints with a typical 10 kg reaction wheel payload was successfully tested at ISRO. It yielded experimental outcomes in close agreement with modelling and analysis
This work underscores the efficacy of the design approach and the suitability of an MGSP for isolating micro-vibrations in spacecraft.