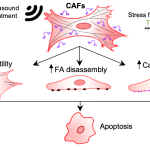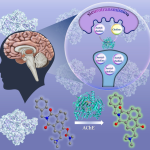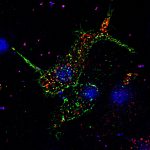
Potential blood-based biomarkers to predict disease progression and survival times in those with late-stage brain tumours have been identified by a team of researchers from IISc, the Mazumdar Shaw Centre for Translational Research and Mazumdar Shaw Medical Foundation.
The team analysed tumour and blood samples from individuals with gliomas – tumours that occur in the brain – to identify surface proteins on immune cells in the blood whose levels were closely linked to tumour progression. This study was published in OncoImmunology.
Late-stage gliomas such as grade three and grade four gliomas are harder to treat and the patient is likely to have a low chance of survival. “Our pilot study suggests that we can potentially use two blood-based biomarkers present on immune cells to identify patients who might not perform well with particular treatment strategies,” says Siddharth Jhunjhunwala, Assistant Professor in the Centre for BioSystems Science and Engineering (BSSE), and senior author of the study.
Such a blood-based testing methodology could help clinicians better understand disease progression and choose a more effective treatment regimen.
The team collected blood and tumour samples from patients with grade three and grade four gliomas, and compared the numbers of specific immune cells called monocytes and neutrophils in these samples.
“Because these are biosamples, they need to be preserved and processed very well without loss of cell viability,” explains Jayashree V Raghavan, PhD student at BSSE and first author of the study. “We had to split up methodology between two institutes – here and at the lab at the Mazumdar Shaw Foundation. They would do all the processing and fixation to retain the viability of the cells, and then we would do the characterisation and immunostaining here.”
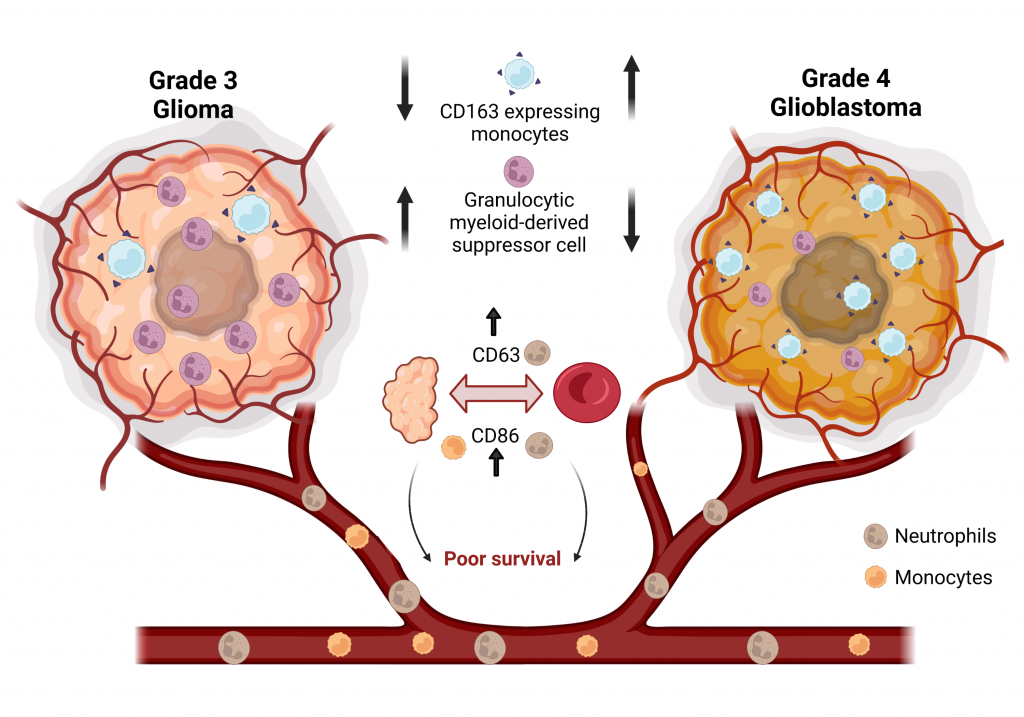
The team also looked for differences in the composition of surface proteins on these cells across the two grades of tumours. They found that a certain type of monocytes – the M2 monocytes – were present in larger numbers in the samples from grade four tumours. Previous studies have shown that high numbers of M2 monocytes are associated with a suppression of immune responses, and this finding could therefore help develop new treatment strategies. “Future studies could focus on developing therapies that reduce the numbers of M2 monocytes in the tumour microenvironment or alter their functionality,” says Jhunjhunwala.
The researchers also found that levels of two surface proteins on neutrophils and monocytes, CD86 and CD63, were closely related in both the blood and tumour samples. The presence of high levels of these proteins on immune cells in other tumours has previously been associated with poor prognosis, or low chances of survival, Jhunjhunwala points out. “What our study showed is that you do not need to look at these markers only in the tumours, you might be able to look at these just from the blood, and the clinician can make an assessment,” he says.
Jhunjhunwala cautions, however, that further testing and validation on a larger scale is necessary before this can be taken from the lab to the clinic. “We would like to expand our cohort and test [for] only these two markers now, in individuals with stage three and stage four brain tumours, and follow their survival times.”